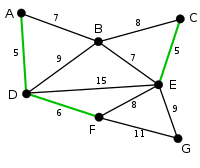
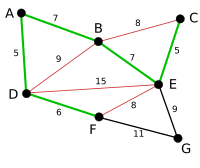
Kruskal's algorithm is a greedy algorithm in graph theory that finds a minimum spanning tree for a connected weighted graph. This means it finds a subset of the edges that forms a tree that includes every vertex, where the total weight of all the edges in the tree is minimized. If the graph is not connected, then it finds a minimum spanning forest (a minimum spanning tree for each connected component).
import java.io.*;
class Tnode
{
char label;
//boolean vis;
int prev;
public Tnode(char lab)
{
label = lab;
//vis=false;
prev=-1;
}
}
class graph
{
public final int MAX = 20;
public int nverts,i,min;
public Tnode vlist[];
public int adj[][];
public graph()
{
nverts = 0;
adj = new int[MAX][MAX];
vlist = new Tnode[MAX];
for(int i=0;i<MAX;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<MAX;j++)
adj[i][j] = 10000;
}
}
public void addver(char lab)
{
vlist[nverts++] = new Tnode(lab);
}
public void addedge(int start,int end,int cost)
{
adj[start][end] = cost;
adj[end][start] = cost;
}
public int getind(char l)
{
for(int i=0;i<nverts;i++)
if(vlist[i].label==l)
return i;
return (MAX+1);
}
boolean find(int i, int j)
{
int a,b,k=0,l=0;
a=i;b=j;
while(a!=-1)
{
k=a;
a=vlist[a].prev;
}
if(a==b)
return false;
a=i;b=j;
while(b!=-1)
{
l=b;
b=vlist[b].prev;
}
if(a==b || k==l)
return false;
return true;
}
public void brfs()
{
int k,c=0,minicost=0,j,mini=100000,m=0,p=0,ct=1;
while(ct<nverts)
{
for(i=0;i<nverts;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<nverts;j++)
{
if((mini>adj[i][j])&&(find(i,j)))
{
mini=adj[i][j];
p=i;
m=j;
}
}
}
System.out.print("\n vertex" +vlist[p].label+"is connected to"+vlist[m].label);
minicost=minicost+mini;
mini=100000;
adj[p][m]=100000;
adj[m][p]=100000;
if(vlist[m].prev==-1)
vlist[m].prev=p;
else
vlist[p].prev=m;
//vlist[m].vis=true;
//vlist[p].vis=true;
ct++;
}
System.out.println("\nMinimum cost=" +minicost);
}
}
class Krus
{
public static void main(String args[])throws IOException
{
graph gr = new graph();
char c;
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
System.out.println("Enter the number of vertices");
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
String t;
System.out.println("Enter the labels for the vertices");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
t = br.readLine();
c = t.charAt(0);
gr.addver(c);
}
System.out.println("Enter the number of edges");
int edg = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println("Enter the vertices which you need to connect");
for(int j=0;j<edg;j++)
{
System.out.println("Enter the first vertex");
t = br.readLine();
c = t.charAt(0);
int start = gr.getind(c);
System.out.println("Enter the second vertex");
t = br.readLine();
c = t.charAt(0);
int end = gr.getind(c);
System.out.println("Enter the cost");
int cost = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
gr.addedge(start,end, cost);
}
gr.brfs();
}
}
Example run
import java.io.*;
class Tnode
{
char label;
//boolean vis;
int prev;
public Tnode(char lab)
{
label = lab;
//vis=false;
prev=-1;
}
}
class graph
{
public final int MAX = 20;
public int nverts,i,min;
public Tnode vlist[];
public int adj[][];
public graph()
{
nverts = 0;
adj = new int[MAX][MAX];
vlist = new Tnode[MAX];
for(int i=0;i<MAX;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<MAX;j++)
adj[i][j] = 10000;
}
}
public void addver(char lab)
{
vlist[nverts++] = new Tnode(lab);
}
public void addedge(int start,int end,int cost)
{
adj[start][end] = cost;
adj[end][start] = cost;
}
public int getind(char l)
{
for(int i=0;i<nverts;i++)
if(vlist[i].label==l)
return i;
return (MAX+1);
}
boolean find(int i, int j)
{
int a,b,k=0,l=0;
a=i;b=j;
while(a!=-1)
{
k=a;
a=vlist[a].prev;
}
if(a==b)
return false;
a=i;b=j;
while(b!=-1)
{
l=b;
b=vlist[b].prev;
}
if(a==b || k==l)
return false;
return true;
}
public void brfs()
{
int k,c=0,minicost=0,j,mini=100000,m=0,p=0,ct=1;
while(ct<nverts)
{
for(i=0;i<nverts;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<nverts;j++)
{
if((mini>adj[i][j])&&(find(i,j)))
{
mini=adj[i][j];
p=i;
m=j;
}
}
}
System.out.print("\n vertex" +vlist[p].label+"is connected to"+vlist[m].label);
minicost=minicost+mini;
mini=100000;
adj[p][m]=100000;
adj[m][p]=100000;
if(vlist[m].prev==-1)
vlist[m].prev=p;
else
vlist[p].prev=m;
//vlist[m].vis=true;
//vlist[p].vis=true;
ct++;
}
System.out.println("\nMinimum cost=" +minicost);
}
}
class Krus
{
public static void main(String args[])throws IOException
{
graph gr = new graph();
char c;
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
System.out.println("Enter the number of vertices");
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
String t;
System.out.println("Enter the labels for the vertices");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
t = br.readLine();
c = t.charAt(0);
gr.addver(c);
}
System.out.println("Enter the number of edges");
int edg = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println("Enter the vertices which you need to connect");
for(int j=0;j<edg;j++)
{
System.out.println("Enter the first vertex");
t = br.readLine();
c = t.charAt(0);
int start = gr.getind(c);
System.out.println("Enter the second vertex");
t = br.readLine();
c = t.charAt(0);
int end = gr.getind(c);
System.out.println("Enter the cost");
int cost = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
gr.addedge(start,end, cost);
}
gr.brfs();
}
}




No comments:
Post a Comment